The Diamond Colour Scale
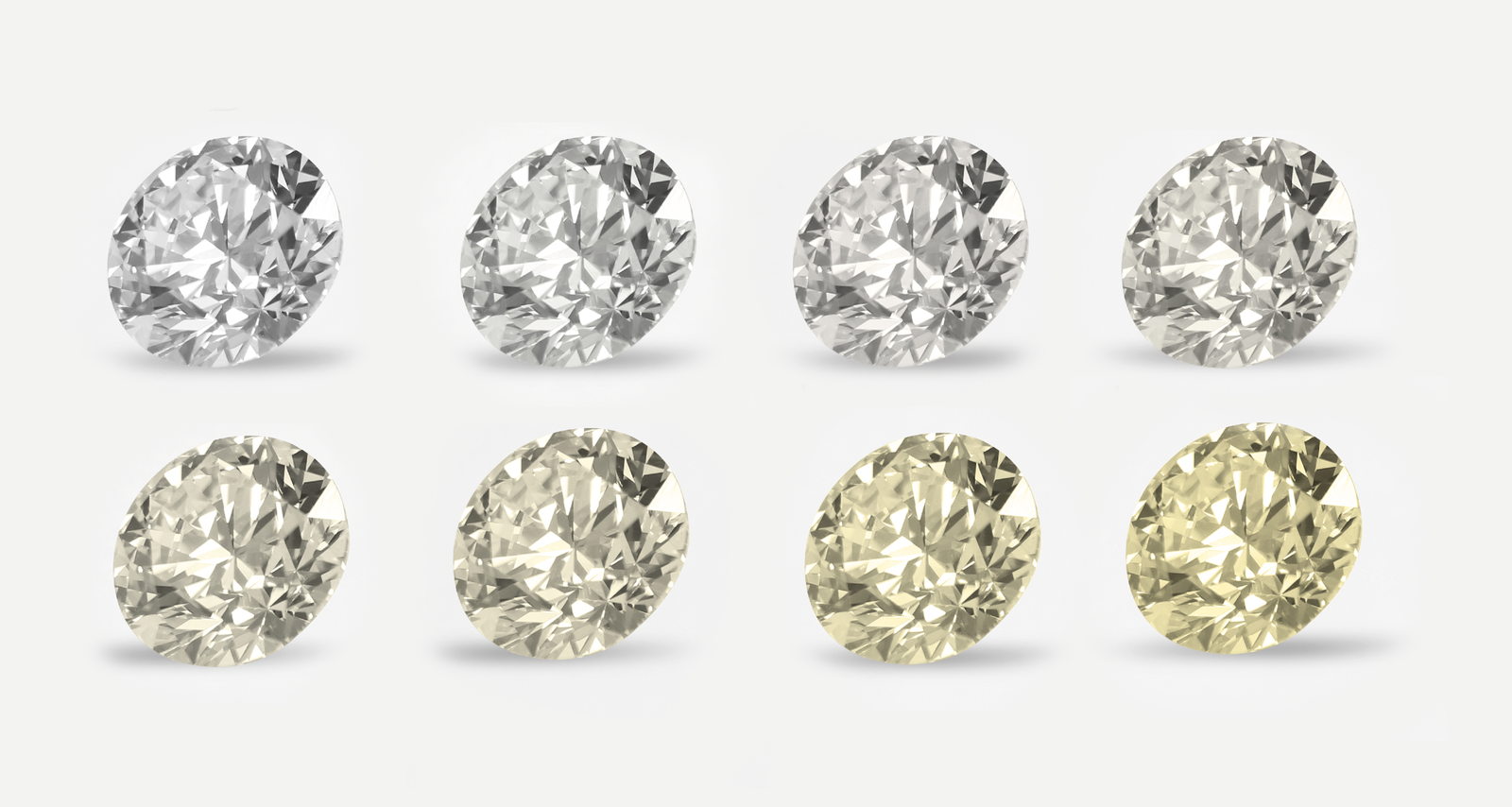
The Gemmological Institute of America (GIA), a renowned authority in gemmology, established the diamond colour scale to objectively assess and grade the colour of diamonds. The scale ranges from D (colourless) to Z (light yellow or brown).
D-F: Colourless
Diamonds in the D to F range are considered colourless. These rare gems exhibit an absence of any noticeable colour, appearing pure and transparent. Their exceptional brightness and fire make them highly coveted and, consequently, more valuable.
G-J: Near Colourless
Diamonds in the G to J range are classified as near colourless. While they may show faint traces of colour, these nuances are typically invisible to the untrained eye. Near colourless diamonds offer an excellent balance of beauty and value, making them a popular choice for engagement rings and other jewellery.
K-M: Faint
Diamonds in the K to M range exhibit a faint yellow or brown tint. While these subtle hues are more noticeable than in higher-grade diamonds, they can still be an appealing option for those seeking a larger stone within a more budget-friendly range.
N-R: Very Light
The diamonds in the N to R range display a very light colour. The presence of colour becomes more apparent, and these diamonds may be suitable for those who prioritise size over colour. However, it's important to note that individual preferences vary, and some may find the warmth of these diamonds charming.
S-Z: Light
Diamonds in the S to Z range are categorised as light in colour. The noticeable presence of yellow or brown tones may impact the overall beauty of the diamond.

*This image is indicative and for illustrative purposes.